CircleCI Android Tutorial
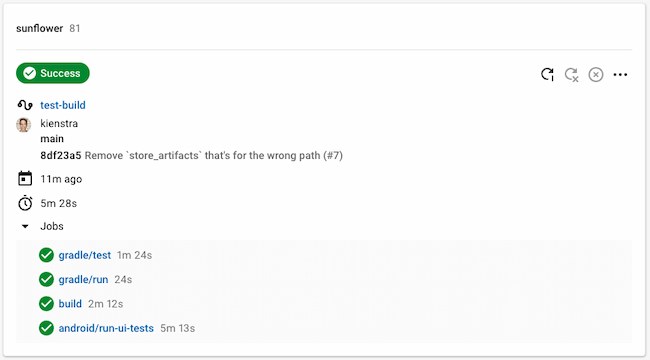
In this CircleCI Android tutorial, you’ll see how to:
- Build an
.apkfile - Lint
- Run unit tests
- Run UI tests
We’ll start by forking an existing Android repo that doesn’t have a CircleCI config:
Then, we’ll add a .circleci/config.yml file, starting with:
The orbs on line 3 make this much easier.
They handle caching, and even run and entire job for you, in the case of the android orb.
Orbs are prepackaged CircleCI jobs or commands that can abstract away details like caching.
Also, the executors stanza on line 7 defines a Docker image that you can reference in jobs.
Building an .apk
Now, let’s add the first job:
Line 14 references the android executor that we just defined.
The steps array at line 15 begins with checkout, which checks out the repo into the CircleCI environment.
Next, we use the gradle/with_cache command from the gradle orb we defined above.
This will cache the gradle packages between jobs:
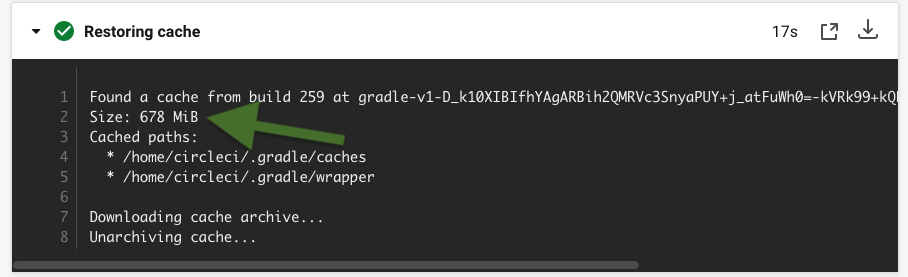
It caches a huge amount of dependencies for you.
678 mebibytes, about 710 megabytes.
And it will run the command ./gradlew -s assembleDebug to build the .apk file of the app.
The store_artifacts value on line 22 makes the build available in CircleCI:
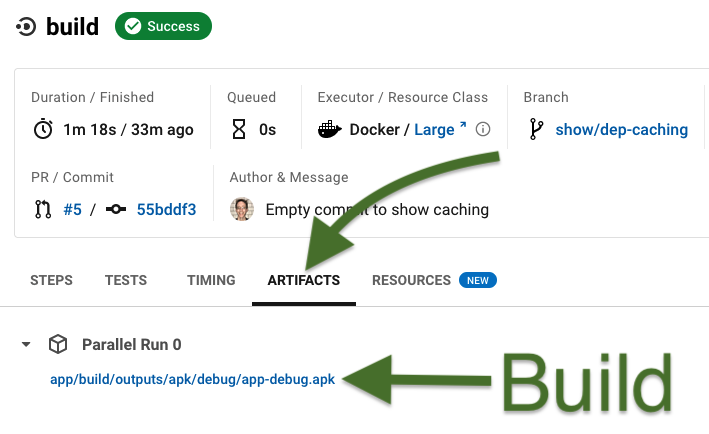
The path might be different for your repo.
Next, we’ll add a workflows stanza and add this build job to it:
Linting
The next jobs are much simpler, thanks to CircleCI orbs.
We’ll simply use the gradle orb for the gradle/run job:
We just need to pass the executor (image), and the command of klint --stacktrace.
This will run linting for us.
Unit Tests
This will also use the gradle orb:
The executor of android adds the Android SDK to the environment.
Without that, the test command will fail.
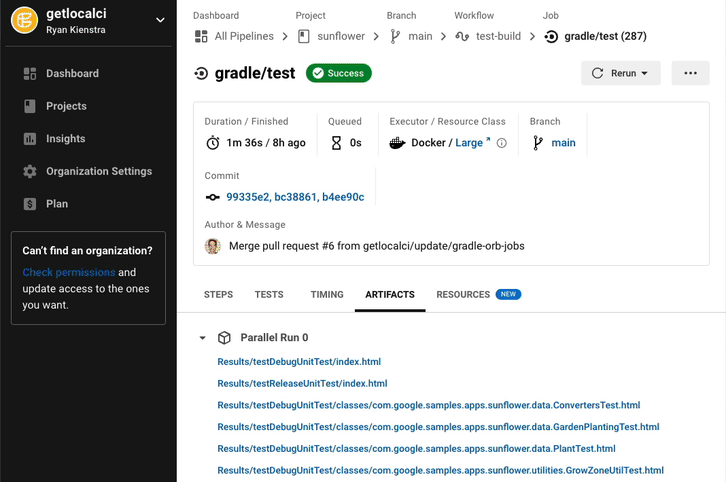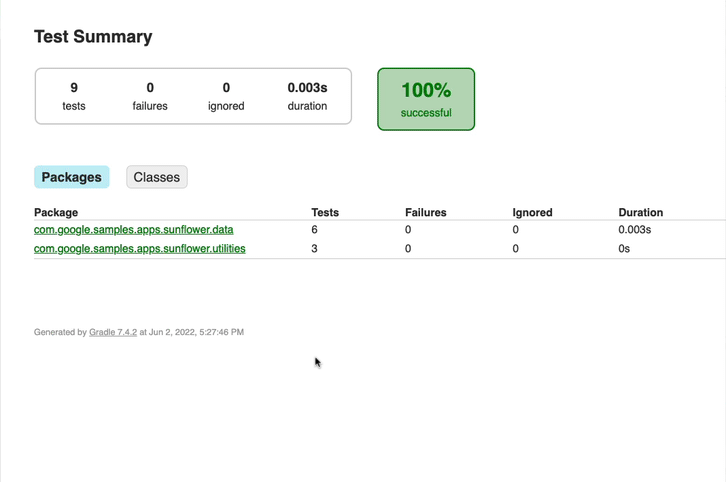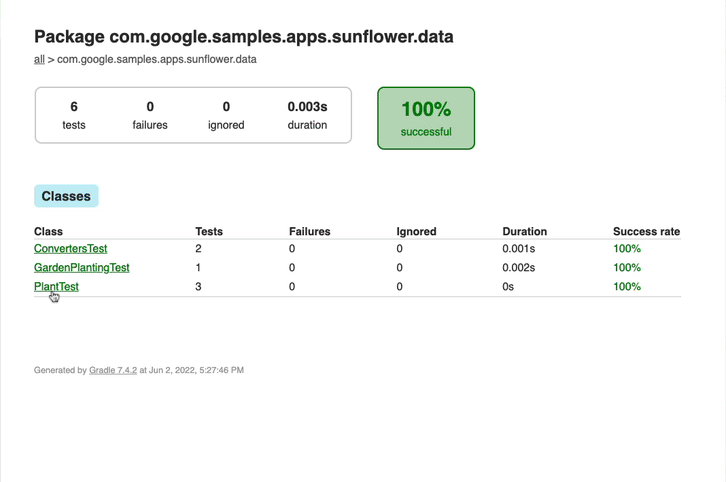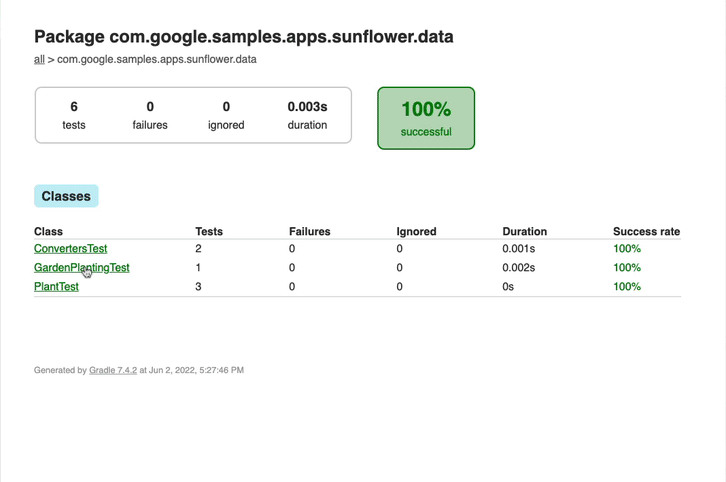
Also, we store the test results with the tests_results_path value.
This lets us see them in CircleCI under the ‘Artifacts’ tab:
UI Tests
In these very complex UI tests, the CircleCI Android orb starts an emulator and does caching.
We avoid a lot of configuration by using that orb’s android/run-ui-tests job:
Like the previous jobs, we pass a ./gradlew command.
CircleCI Android Tutorial
Here’s the final config.yml:
And we see all 4 jobs passing:
